[문제]
아래의 6개의 클래스를 작성하고, 메인에서 아래와 같은 실행결과를 출력하시오(다형성)
Shape,Circle,Rectangle,Triangle,Node,ShapeExample
(각각 "Shape", "Circle", "Rectangle", "Traingle" 이라 출력하는 기능을 가지고 있다. 이 클래스들을 이용하여 아래 그림1과 같이 연결 리스트로 구성한 후, 아래와 같이 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하라. * 단, 다형성을 구현하는 프로그램으로 작성하라. )
Shape Class(조상클래스)
멤버함수
void paint()
void draw()
*main에서 pStart와 pLast를 사용하자!
실행화면
1.Circle 2.Triangle 3.Rectangle 4.Print 5.Exit : 1
Circle이 연결됨.
1.Circle 2.Triangle 3.Rectangle 4.Print 5.Exit : 3
Rectangle이 연결됨.
1.Circle 2.Triangle 3.Rectangle 4.Print 5.Exit : 1
Circle이 연결됨.
1.Circle 2.Triangle 3.Rectangle 4.Print 5.Exit : 2
Triangle이 연결됨.
1.Circle 2.Triangle 3.Rectangle 4.Print 5.Exit : 3
Rectangle이 연결됨.
1.Circle 2.Triangle 3.Rectangle 4.Print 5.Exit : 4
Circle->Rectangle->Circle->Triangle->Rectangle
5개의 도형이 생성되었습니다.
1.Circle 2.Triangle 3.Rectangle 4.Print 5.Exit : 5
종료합니다.
[답안]
노드 없는 구조
//RE 1.2.3
class Shape {
Shape Next;
void paint() {
draw();
}
void draw() {
System.out.print("Shape을 만듭니다.");
}
}
class Circle extends Shape {
void draw() {
System.out.print("Circle");
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
void draw() {
System.out.print("Rectangle");
}
}
class Triangle extends Shape {
void draw() {
System.out.print("Triangle");
}
}
class ShapeExample {
void run() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Shape pStart = null;
Shape pLast = null;
while (true) {
System.out.print("1.Circle 2.Triangle 3.Rectangle 4.Print 5.Exit : ");
int num = sc.nextInt();
if (num == 1) {
Shape newShape = new Circle();
if (pStart == null) {
pStart = newShape;
pLast = pStart;
} else {
pLast.Next = newShape;
pLast = newShape;
}
pLast.paint();
System.out.println("이 연결됨.");
System.out.println();
}
else if (num == 2) {
Shape newShape = new Triangle();
if (pStart == null) {
pStart = newShape;
pLast = pStart;
} else {
pLast.Next = newShape;
pLast = newShape;
pLast.paint();
System.out.println("이 연결됨.");
System.out.println();
}
}
else if (num == 3) {
Shape newShape = new Rectangle();
if (pStart == null) {
pStart = newShape;
pLast = pStart;
} else {
pLast.Next = newShape;
pLast = newShape;
}
pLast.paint();
System.out.println("이 연결됨.");
System.out.println();
}
else if (num == 4) {
int n = 0;
for (Shape cur = pStart; cur != null; cur = cur.Next, n++) {
cur.paint();
if (cur.Next == null)
continue;
System.out.print("->");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(n + "개의 도형이 생성되었습니다.");
System.out.println();
}
else if (num == 5) {
System.out.println("종료합니다.");
break;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapeExample shape = new ShapeExample();
shape.run();
}
}기본 코드는 이렇다.

객체를 생성할 때 else 문을 안 넣어줘도 되긴 하지만 처음 객체가 하나일 때 이렇게 Next를 사용할 필요가 없으므로 else 처리를 해주는 것이 낫다.
Shape pStart = null;
Shape pLast = null;
이 코드는 꼭 while 문 바깥에 선언해 주자.
노드 있는 구조
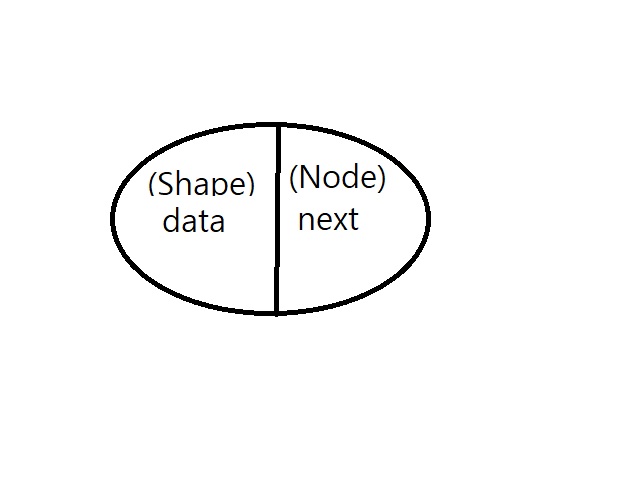
class Shape {
//Shape Next;
void paint() {
draw();
}
void draw() {
System.out.print("Shape을 만듭니다.");
}
}
class Circle extends Shape {
void draw() {
System.out.print("Circle");
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
void draw() {
System.out.print("Rectangle");
}
}
class Triangle extends Shape {
void draw() {
System.out.print("Triangle");
}
}
class Node {
Shape data;
Node Next;
public Node(Shape data,Node Next) {
this.data=data;
this.Next=Next;
}
}
class ShapeExample {
void run() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Node pStart = null;
Node pLast = null;
while (true) {
System.out.print("1.Circle 2.Triangle 3.Rectangle 4.Print 5.Exit : ");
int num = sc.nextInt();
if (num == 1) {
Shape newShape = new Circle();
Node newNode = new Node(newShape,null);
if (pStart == null) {
pStart = newNode;
pLast = pStart;
} else {
pLast.Next = newNode;
pLast = newNode;
}
pLast.data.paint();
System.out.println("이 연결됨.");
System.out.println();
}
else if (num == 2) {
Shape newShape = new Triangle();
Node newNode = new Node(newShape,null);
if (pStart == null) {
pStart = newNode;
pLast = pStart;
} else {
pLast.Next = newNode;
pLast = newNode;
}
pLast.data.paint();
System.out.println("이 연결됨.");
System.out.println();
}
else if (num == 3) {
Shape newShape = new Rectangle();
Node newNode = new Node(newShape,null);
if (pStart == null) {
pStart = newNode;
pLast = pStart;
} else {
pLast.Next = newNode;
pLast = newNode;
}
pLast.data.paint();
System.out.println("이 연결됨.");
System.out.println();
}
else if (num == 4) {
int n = 0;
for (Node cur = pStart; cur != null; cur = cur.Next, n++) {
cur.data.paint();
if (cur.Next == null)
continue;
System.out.print("->");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(n + "개의 도형이 생성되었습니다.");
System.out.println();
}
else if (num == 5) {
System.out.println("종료합니다.");
break;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapeExample shape = new ShapeExample();
shape.run();
}
}
Shape newShape = new Circle();
Node newNode = new Node(newShape,null);는 Node newNode = new Node(new Circle(),null);과 같이 한 줄로도 수정 가능하다.
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] (추상 클래스) (16-2) (0) | 2023.08.30 |
|---|---|
| [Java] (추상 클래스) (16-1) (0) | 2023.08.30 |
| [Java] 클래스 (상속, 오버라이딩, 다형성, 스택, 팝) (15) (0) | 2023.08.27 |
| [Java] 단축키 (0) | 2023.08.24 |
| [Java] 상속과 다형성 문제 (0) | 2023.08.18 |
